3 in stock
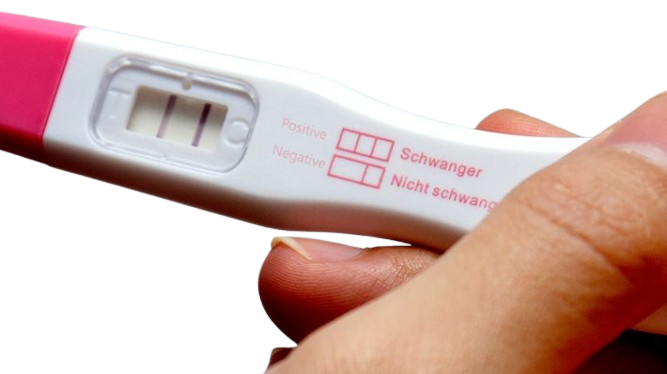
CONCEPTIONCHECK PREGNANCY PEE STICK
A pregnancy test is used to determine whether a female is pregnant or not. The two primary methods are testing for the female pregnancy hormone (human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)) in blood or urine using a pregnancy test kit, and scanning with ultrasonography. Testing blood for hCG results in the earliest detection of pregnancy. Almost all pregnant women will have a positive urine pregnancy test one week after the first day of a missed menstrual period.
Pregnancy tests may be used to predict if a pregnancy is likely to continue or is abnormal. Miscarriage, or spontaneous abortion or pregnancy loss, is common in early pregnancy. Serial quantitative blood tests may be done, usually 48 hours apart, and interpreted based on the knowledge that hCG in a viable normal pregnancy rises rapidly in early pregnancy. For example, for a starting hCG level of 1,500 mIU/ml or less, the hCG of continuing, normal pregnancy will increase at least 49% in 48 hours. However, for pregnancies with a higher starting hCG, between 1,500 and 3,000 mIU/ml, the hCG should rise at least 40%; for a starting hCG greater than 3,000 mIU/ml, the hCG should increase at least 33%. Failure to rise by these minimums may indicate that the pregnancy is not normal, either as a failed intrauterine pregnancy or a possible ectopic pregnancy.
Ultrasound is also a common tool for determining viability and location of a pregnancy. Serial ultrasound may be used to identify non-viable pregnancies, as pregnancies that do not grow in size or develop expected structural findings on repeated ultrasounds over a 1-2 week interval may be identified as abnormal.
Occasionally, a single ultrasound may be used to identify a pregnancy as non-viable; for example, an embryo that is greater than a certain size but that lacks a visible heart beat may be confidently determined to be not viable without the need for follow up ultrasound for confirmation.
₦2,340.00
A pregnancy test is used to determine whether a female is pregnant or not. The two primary methods are testing for the female pregnancy hormone (human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)) in blood or urine using a pregnancy test kit, and scanning with ultrasonography. Testing blood for hCG results in the earliest detection of pregnancy. Almost all pregnant women will have a positive urine pregnancy test one week after the first day of a missed menstrual period.
Pregnancy tests may be used to predict if a pregnancy is likely to continue or is abnormal. Miscarriage, or spontaneous abortion or pregnancy loss, is common in early pregnancy. Serial quantitative blood tests may be done, usually 48 hours apart, and interpreted based on the knowledge that hCG in a viable normal pregnancy rises rapidly in early pregnancy. For example, for a starting hCG level of 1,500 mIU/ml or less, the hCG of continuing, normal pregnancy will increase at least 49% in 48 hours. However, for pregnancies with a higher starting hCG, between 1,500 and 3,000 mIU/ml, the hCG should rise at least 40%; for a starting hCG greater than 3,000 mIU/ml, the hCG should increase at least 33%. Failure to rise by these minimums may indicate that the pregnancy is not normal, either as a failed intrauterine pregnancy or a possible ectopic pregnancy.
Ultrasound is also a common tool for determining viability and location of a pregnancy. Serial ultrasound may be used to identify non-viable pregnancies, as pregnancies that do not grow in size or develop expected structural findings on repeated ultrasounds over a 1-2 week interval may be identified as abnormal.
Occasionally, a single ultrasound may be used to identify a pregnancy as non-viable; for example, an embryo that is greater than a certain size but that lacks a visible heart beat may be confidently determined to be not viable without the need for follow up ultrasound for confirmation.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.